𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Loss of productivity, disturbance, hindrance or interruption to contractor’s normal working methods, resulting lower efficiency
𝐈𝐬 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞?
If caused by Employer, it may give right to compensation either under contract or as breach of contract. However, you should know that
𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐌𝐚𝐲 𝐋𝐞𝐚𝐝 𝐓𝐨 𝐋𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐁𝐮𝐭 𝐍𝐨𝐭 𝐍𝐞𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐥𝐲 𝐒𝐨
It’s possible for work to be disrupted & for contract still to finish by contract completion date. In this situation
“𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐧’𝐭 𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐜𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐄𝐎𝐓, 𝐛𝐮𝐭 𝐦𝐚𝐲 𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐜𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐫𝐞𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐲 𝐨𝐟 𝐢𝐭𝐬 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐜𝐞”
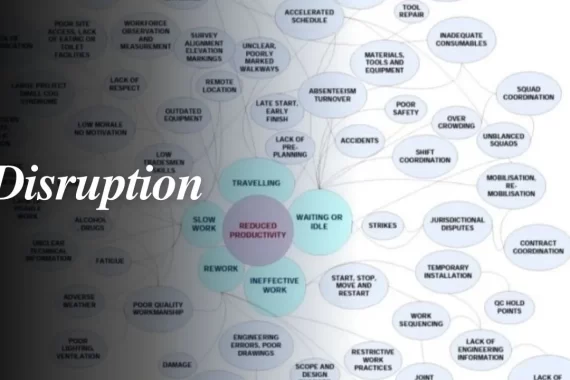
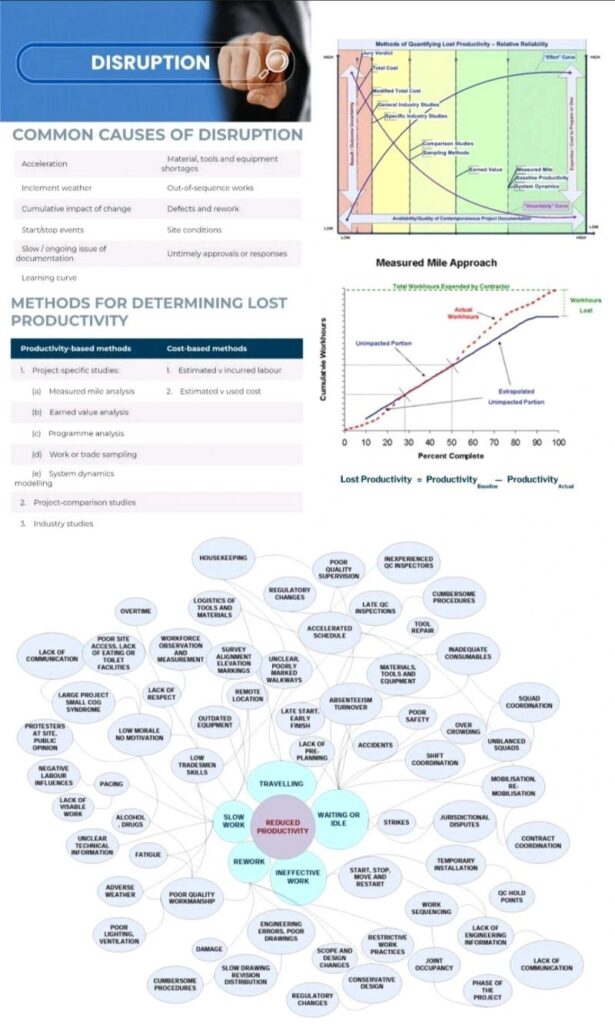
𝐂𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧:
•Changes to working methods
•Changes to working conditions & sequence
Ex. change in sequence or priority of work making some works more onerous to perform
•Adverse weather
•Management characteristics
•Project characteristics
Contractor should provide evidence regarding:
1-Disrupted Trade/work progress
2-Impacted (when disrupted) & unimpacted period(s) on work
3-Additional manpower (& equipment) expended on disrupted trades
4-Evaluate difference between periods analysed
5-Events caused work disruption
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
It’s not easy to prove disruptions especially without very detailed records as this is your strongest method to prove disruption by keeping good records
A side form keeping a good records, contractor has to focus on Cause by identify & track through to effect
Disruption exists on Micro level:
•It takes place within working day
•It may come down to lost hours or minutes within a day
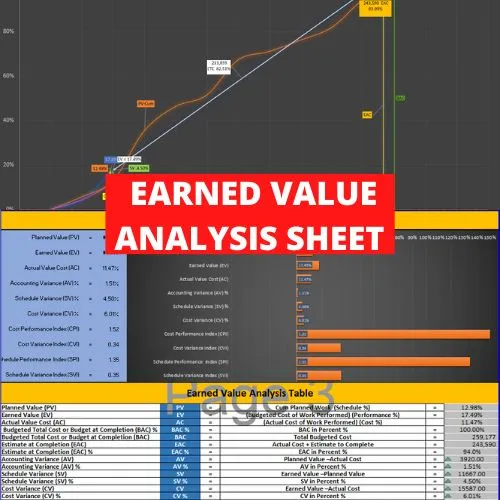
Common Disruption Quantification methods used to measure disruption
-Baseline productivity analysis
-Earned value analysis (EVA)
-Measured mile analysis
●𝐌𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐝 𝐌𝐢𝐥𝐞 𝐀𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬
Widely acknowledged as most acceptable method for calculating lost productivity costs
Analysis compares identical tasks in impacted & non-impacted periods of project to estimate productivity loss caused by impact of known series of events
Attraction of measured mile is that it compares actual performance on site with actual performance, not some theoretical planned performance
Productivity Change =
Unit Productivity during Impacted Period/Unit Productivity during Un-impacted Period
“There’s no fixed calculation method. But same principle applies, it’s very much dependent on nature of tasks as well as data available”
Calculation steps:
1》Identify Period Of Impeded Performance
2》Calculate Performance Ratio for Impeded Period
3》Calculate Performance Ratio for Un-impeded Period
4》Calculate difference between Performance Ratios
5》For disruption during Impeded Period:
Additional Cost or Resource to achieve a task due to Disruption = Performance Ratios X Planned Value Earned during Impeded PeriodLoss of productivity, disturbance, hindrance or interruption to contractor’s normal working methods, resulting lower efficiency
𝐈𝐬 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞?
If caused by Employer, it may give right to compensation either under contract or as breach of contract. However, you should know that
𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐌𝐚𝐲 𝐋𝐞𝐚𝐝 𝐓𝐨 𝐋𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐁𝐮𝐭 𝐍𝐨𝐭 𝐍𝐞𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐥𝐲 𝐒𝐨
It’s possible for work to be disrupted & for contract still to finish by contract completion date. In this situation
“𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐧’𝐭 𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐜𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐄𝐎𝐓, 𝐛𝐮𝐭 𝐦𝐚𝐲 𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐜𝐥𝐚𝐢𝐦 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐫𝐞𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐲 𝐨𝐟 𝐢𝐭𝐬 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐜𝐞”
𝐂𝐚𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧:
•Changes to working methods
•Changes to working conditions & sequence
Ex. change in sequence or priority of work making some works more onerous to perform
•Adverse weather
•Management characteristics
•Project characteristics
Contractor should provide evidence regarding:
1-Disrupted Trade/work progress
2-Impacted (when disrupted) & unimpacted period(s) on work
3-Additional manpower (& equipment) expended on disrupted trades
4-Evaluate difference between periods analysed
5-Events caused work disruption
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐃𝐢𝐬𝐫𝐮𝐩𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
It’s not easy to prove disruptions especially without very detailed records as this is your strongest method to prove disruption by keeping good records
A side form keeping a good records, contractor has to focus on Cause by identify & track through to effect
Disruption exists on Micro level:
•It takes place within working day
•It may come down to lost hours or minutes within a day
Common Disruption Quantification methods used to measure disruption
-Baseline productivity analysis
-Earned value analysis (EVA)
-Measured mile analysis
●𝐌𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐝 𝐌𝐢𝐥𝐞 𝐀𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬
Widely acknowledged as most acceptable method for calculating lost productivity costs
Analysis compares identical tasks in impacted & non-impacted periods of project to estimate productivity loss caused by impact of known series of events
Attraction of measured mile is that it compares actual performance on site with actual performance, not some theoretical planned performance
Productivity Change =
Unit Productivity during Impacted Period/Unit Productivity during Un-impacted Period
“There’s no fixed calculation method. But same principle applies, it’s very much dependent on nature of tasks as well as data available”
Calculation steps:
1》Identify Period Of Impeded Performance
2》Calculate Performance Ratio for Impeded Period
3》Calculate Performance Ratio for Un-impeded Period
4》Calculate difference between Performance Ratios
5》For disruption during Impeded Period:
Additional Cost or Resource to achieve a task due to Disruption = Performance Ratios X Planned Value Earned during Impeded Period
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.